Your basement fills with ankle-deep water during last night’s storm. The washing machine floats like a plastic toy, and family photos curl at the edges. This nightmare happens to 14,000 Americans daily—but it doesn’t have to happen to you. While floods cause $20 billion in annual damage, most home flooding is preventable through strategic preparation and maintenance. Understanding how to prevent flooding in home starts with recognizing that 25% of all flood damage claims come from low-risk areas previously considered safe.
This guide transforms proven flood prevention strategies into actionable steps you can implement today. From assessing your specific flood risk to installing the right water management systems, you’ll learn exactly how to protect your home and belongings from water damage. Don’t wait for disaster to strike—take control of your home’s flood resilience starting now.
Pinpoint Your Exact Flood Vulnerabilities

Before buying flood barriers or sump pumps, understand your home’s unique weaknesses. One in four flood claims come from areas previously considered safe, making precise risk assessment crucial for every homeowner.
Decode FEMA Flood Maps Correctly
Visit FEMA’s Flood Map Service Center and enter your address to determine your flood zone designation and Base Flood Elevation (BFE)—the water level expected during a 100-year flood. Properties in A or V zones face the highest risk, while X zones have reduced but still present danger. Remember that climate change has expanded many flood zones since older maps were created, so always check for recent updates.
Pro Tip: Look for discrepancies between FEMA maps and modern risk tools like ClimateCheck or First Street Foundation’s Flood Factor. These platforms combine climate projections with local data to show your home’s 30-year flood probability, often revealing underestimated risks.
Conduct a Property Walk-Through During Rain
Your most accurate flood assessment happens when it’s actually raining. Walk your property during heavy precipitation and watch where water pools, how quickly it drains, and whether it approaches your foundation. Document any basement dampness, gutter overflow, or sewer backups. These real-time observations reveal your home’s specific weak points better than any online tool ever could.
Install Foundation Water Defenses That Work

Poorly insulated foundations represent the most common cause of basement flooding. Address these vulnerabilities before water finds its way inside.
Create Proper Landscape Grading
Ensure ground slopes 6 inches down for every 10 feet away from your foundation. This seemingly minor slope creates a 5-foot drop across a 50-foot yard—enough to move thousands of gallons during storms. Test your grading by placing a hose at your foundation on dry soil; water should flow away immediately. If it pools, add soil or create swales.
Critical Maintenance: Keep mulch 6 inches from siding to prevent moisture wicking and rot. Use pine bark nuggets instead of shredded mulch near foundations—they resist floating and wash away less during heavy rains.
Seal Foundation Cracks Immediately
Address visible cracks wider than 1/8 inch with hydraulic cement or epoxy injections. These materials expand as they cure, creating watertight seals that prevent water entry even under pressure. Don’t ignore hairline cracks—water pressure can quickly widen them during heavy rainfall events.
Optimize Your Water Drainage System
Overflowing gutters dump 1,900 gallons during a 1-inch rainfall on typical roofs. This water saturates soil and creates hydrostatic pressure against basement walls.
Clean Gutters Every Season
Remove leaves, pine needles, and debris from gutters quarterly. Pay special attention to valleys and downspout connections where clogs form first. In wooded areas, install gutter guards—but still inspect them semi-annually. Remember that even with guards, heavy debris accumulation can overwhelm your system.
Pro Installation: Extend downspouts at least 4 feet from your foundation using rigid extensions ($15-30) that slope correctly away from your home. For permanent solutions, consider burying 4-inch PVC pipes sloping 1/8 inch per foot toward street drains or dry wells.
Install Functional Backflow Valves
Sewer backups during floods create health hazards and extensive damage. Install automatic ball float valves in floor drains to stop sewer water from entering your home. For properties with frequent backups, consider gate-style valves that provide better seals but require manual operation.
Critical Note: Standard valves prevent sewage from leaving your home during backups. Add ejector pump attachments to maintain toilet function during extended outages.
Protect Critical Home Systems from Water Damage

Elevated utilities survive floods that destroy ground-level equipment. This prevents $10,000+ replacement costs and maintains basic services during recovery.
Raise Essential Equipment Above Flood Level
Elevate furnaces, water heaters, and electrical panels at least 12 inches above projected flood levels. Build masonry platforms or relocate equipment to higher floors when possible. Secure fuel tanks with non-corrosive metal straps to prevent floating and breaking supply lines during flood events.
Emergency Prep: Document shutoff valve locations with photos and written instructions. Post this information near main electrical panels and ensure all family members understand emergency procedures. During floods, quick shutoffs prevent electrocution and gas explosion risks.
Maintain Plumbing Systems to Avoid Catastrophic Leaks
Burst pipes cause 250,000 floods annually, often during winter storms when homes are unoccupied. Prevent these disasters with regular maintenance.
Replace High-Risk Plumbing Components
Swap rubber washing machine hoses for braided steel versions every 5 years. Inspect water heaters annually for leaks and corrosion—replace units older than 12 years proactively. Monitor water pressure regularly; install pressure regulators if readings exceed 60 PSI.
Winter Checklist:
– Disconnect garden hoses and install freeze-proof spigots
– Insulate pipes in attics, basements, and exterior walls
– Know your water main shutoff location
Install Smart Leak Detection
Place wireless sensors near water heaters, washing machines, and under sinks. Modern systems send smartphone alerts and can automatically shut off water mains when leaks are detected. For comprehensive protection, invest in whole-house systems ($500-1,500) that monitor your entire plumbing network.
Create Landscape Features That Absorb Water
Hard surfaces channel water toward your home. Permeable materials and water-absorbing features reduce runoff volume and velocity.
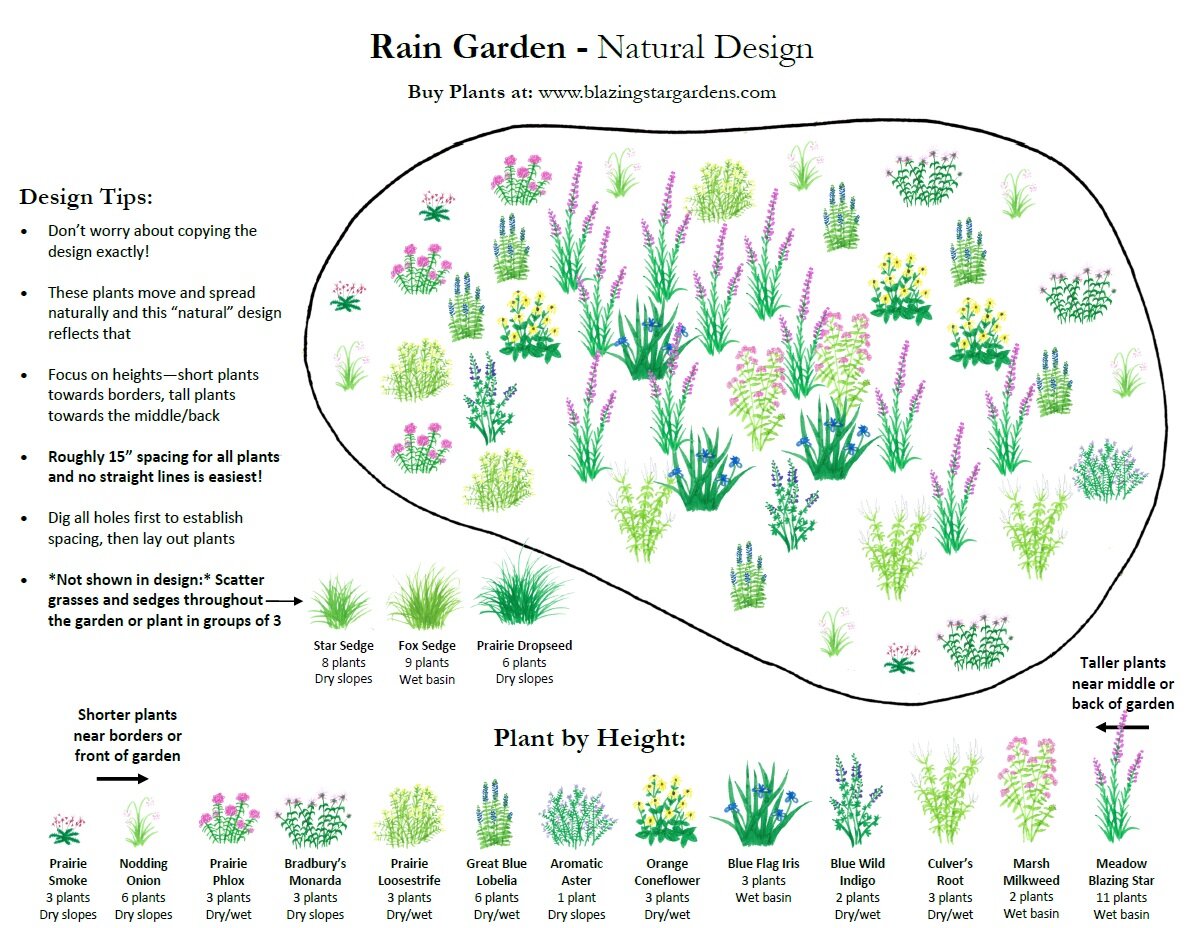
Build Effective Rain Gardens
Create shallow depressions planted with native grasses and flowers 10+ feet from foundations to intercept roof runoff. Size gardens to handle 1 inch of runoff from contributing surfaces—typically 20-30% of roof area. Use native species like switchgrass, purple coneflower, and sedges that tolerate both drought and flooding.
Seasonal Note: Empty rain barrels before winter to prevent ice damage. In cold climates, use removable downspout extensions during freezing months.
Prepare Emergency Response Plans Before Disaster Strikes
Even perfect prevention can fail during extreme events. Quick response minimizes damage and speeds recovery.
Assemble Flood Response Kits
Gather essential supplies before storm season:
– Water: 1 gallon per person per day for 3 days
– Tools: Wrenches for gas/water shutoffs, plastic sheeting, duct tape
– Electronics: Battery radio, phone chargers, flashlights
– Documents: Store copies in waterproof containers or cloud storage
Document Your Property Thoroughly
Create photo/video inventories of all possessions, including serial numbers and receipts. Upload copies to cloud storage. This documentation accelerates insurance claims and ensures fair compensation for losses after flood events.
Address Seasonal Flood Challenges Proactively
Flood risks change with seasons, requiring adjusted preparation strategies throughout the year.
Winter Pipe Protection
Insulate pipes in attics, basements, and exterior walls with foam sleeves. During extreme cold, let faucets drip and maintain indoor temperatures above 55°F. Open cabinet doors under sinks to allow warm air circulation. Monitor sump pump discharge lines for freezing—use freeze-resistant materials or bury below frost lines.
Spring Thaw Readiness
Schedule early inspections of all systems before spring rains begin. Clear roof valleys of ice dams that redirect water toward foundations. Test sump pumps before the rainy season and ensure discharge pipes extend far enough to prevent recirculation.
Your Next Steps: Start with a 30-minute property walk during the next rainstorm. Identify obvious problem areas, then schedule professional inspections for foundation, roofing, and plumbing systems. Begin with the lowest-cost, highest-impact improvements—cleaning gutters costs $0 but prevents thousands in damage. Every month you delay increases your flood risk as climate patterns intensify. Your dry basement tomorrow depends on actions you take today.