When winter storms knock out power for days, your home’s temperature plummets fast—dropping 10-15 degrees in just hours. Knowing how to heat home without electricity isn’t just about comfort; it’s critical for preventing frozen pipes and hypothermia during extended outages. This guide delivers actionable solutions tested in real blackouts, from emergency fixes you can implement tonight to permanent systems that provide year-round energy independence. You’ll discover how to leverage free solar energy, repurpose common household items, and select the safest off-grid heating systems for your climate.
Solar Heat Strategies That Work During Blackouts
Positioning Windows for Maximum Winter Heat Gain
South-facing windows in the Northern Hemisphere capture the most solar energy during cold months—positioning furniture to block window access cuts heating potential by 30%. Install black-painted water barrels near these windows to absorb daytime heat; each 55-gallon drum releases stored warmth for 6-8 hours after sunset. Close thermal curtains over windows at night to trap this heat, reducing heat loss through glass by up to 40%.
Building Emergency Solar Air Heaters
Create a DIY solar heater using a metal box painted black with a glass front and vents at top/bottom. Position it on a south-facing exterior wall: cold air enters the bottom vent, heats as it rises through the box, and exits warm air at the top into your room. On sunny winter days, this simple system can raise indoor temperatures by 15-20°F without any electricity—just ensure it’s securely mounted and never blocks emergency exits.
Wood-Burning Solutions That Heat 2,000 Sq Ft Safely
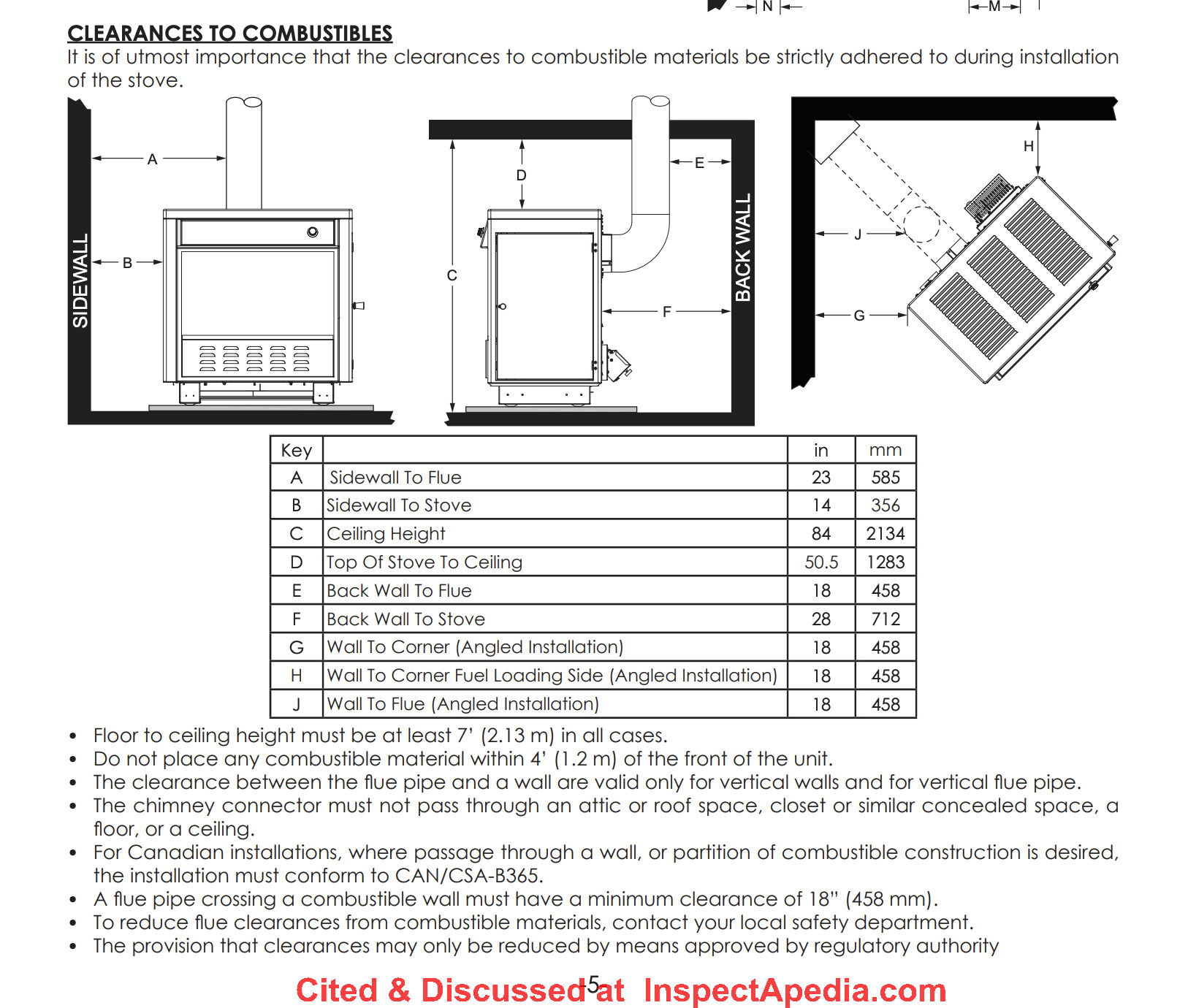
Choosing EPA-Certified Stoves Over Open Fireplaces
Modern EPA-certified wood stoves deliver 70-80% efficiency compared to fireplaces’ 10-15% waste, meaning you use 70% less wood for the same warmth. Never operate a fireplace without installing glass doors—they prevent dangerous heat loss up the chimney while reducing smoke emissions by 60%. For whole-house heating, select a stove rated for your square footage: a 1,500 sq ft home requires at least a 60,000 BTU model with proper clearance from combustibles.
Mastering Pellet Stove Operation During Outages
Pellet stoves provide automated heat without grid power when equipped with battery backups. Stockpile 40-pound bags of compressed wood pellets—each bag delivers 24-48 hours of continuous heat. Critical safety step: Manually operate the auger feed during outages by turning off the thermostat and using the manual override lever. Empty ash pans weekly to prevent fire hazards, and store pellets in airtight metal containers to avoid moisture swelling that jams the feed mechanism.
Emergency Room Heating Within 30 Minutes
Creating Indoor Heat Islands with Blankets and Tarps
When power fails, immediately convert one room into a heat sanctuary:
– Seal all gaps under doors with rolled towels
– Hang heavy blankets over windows at night
– Drape plastic sheeting over doorways to unused rooms
– Set up a family-sized tent inside using sheets and clotheslines
This microclimate traps body heat, making a single room 10-15°F warmer than the rest of your house. Multiple people sharing the space amplify warmth through collective body heat—ideal for sleeping areas during extended outages.
Homemade Water Bottle Heaters for Bedtime Warmth
Heat water on your gas stove (if available) and fill clean plastic bottles, wrapping each in a towel to prevent burns. Place two bottles at your feet and one against your core under blankets—they’ll stay warm for 2-3 hours. Never use glass bottles as they may shatter from thermal shock. For extended warmth, add a pinch of salt to the water before heating—it raises the boiling point and extends heat retention by 20%.
Thermal Mass Techniques That Release Heat All Night

Using Phase-Change Materials for Consistent Temperatures
Strategic placement of thermal mass materials stabilizes indoor temperatures without electricity:
– Soapstone bricks: Position near wood stoves to absorb heat, radiating 12+ hours of warmth
– Water-filled containers: Paint 5-gallon buckets black and place in sunlit windows
– Clay tiles: Install under carpets in sun-drenched rooms to store daytime heat
These materials absorb excess heat when temperatures rise, then slowly release it as rooms cool—reducing temperature swings by up to 10°F. For best results, combine with south-facing windows to maximize solar charging during daylight hours.
Biological Heat Sources Most People Overlook
Harnessing Compost Heat Through Simple Piping
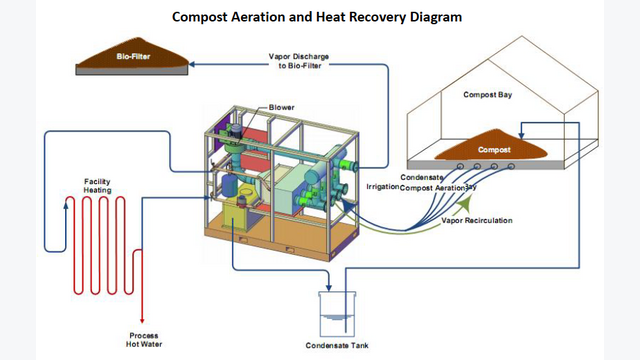
Large compost piles (minimum 3x3x3 feet) generate 130-160°F from microbial activity. Bury coiled food-grade hoses in your compost heap, connecting them to radiators in your home. Circulate water through this loop using gravity feed—no pumps needed. Warning: Maintain 18-inch separation between compost pipes and living spaces to prevent odor infiltration. This system works best with consistent organic input: plan for 20+ cubic yards of compost for meaningful home heating.
Strategic Animal Heat Integration for Rural Homes
Positioning livestock housing adjacent to living areas captures natural body heat:
– Chickens in insulated coops add 5-7°F to connected spaces
– Goats or sheep barns can raise temperatures by 8-10°F
– Always separate animal areas with vapor barriers to prevent moisture damage
This method requires careful ventilation planning—install passive air vents at opposite ends to maintain airflow while trapping warmth. Works best in sub-zero climates where the heat differential is greatest.
Critical Safety Protocols for Non-Electric Heat
Avoiding Carbon Monoxide Poisoning During Outages
Every combustion heater requires fresh air intake—never seal rooms completely. Install battery-operated CO detectors on every level of your home and test them monthly. When using alcohol heaters or propane devices:
– Crack a window 1 inch for ventilation
– Place heaters on non-flammable surfaces 3+ feet from combustibles
– Never sleep with unvented fuel-burning devices operating
Remember: charcoal grills and camp stoves produce lethal CO levels indoors—use them only outside with 20+ feet clearance from windows.
Fire Prevention with Wood and Pellet Systems
Maintain strict clearances around heating appliances:
– Wood stoves: 36-inch minimum from walls/furniture
– Pellet stove exhaust vents: 48-inch clearance from combustibles
– Spark guards: Always use when stove is operating
Store firewood outdoors on elevated racks covered with tarp (never against your house). Clean stovepipes monthly during heating season—creosote buildup causes 25% of home heating fires.
Long-Term System Selection for Your Climate
Matching Heating Solutions to Regional Conditions
Choose systems based on your specific environment:
– Sunny climates: Prioritize solar thermal systems (50-70% heating cost reduction)
– Forested areas: Invest in EPA-certified wood stoves with thermal mass storage
– Moderate zones: Geothermal heat exchangers work best where ground temps stay 50-55°F
– Frequent outages: Combine pellet stove with solar battery backup
Key mistake to avoid: Installing solar systems in regions with less than 4 daily sunshine hours—supplement with wood heat instead. Always get professional site assessments before major installations.
Immediate Action Plan for Power Outages
Start tonight with these outage-ready preparations:
1. Stock emergency heat sources: Keep 5 alcohol heater fuel bottles (lasts 15+ hours)
2. Pre-position thermal mass: Place water jugs near south windows before winter
3. Seal your heat sanctuary: Keep draft-stopping towels and plastic sheeting ready
4. Test ventilation: Verify window-cracking strategy won’t cause freezing pipes
During an outage: Focus heat in one room, use water bottle heaters for beds, and run brief exercise sessions to boost body temperature. Never risk carbon monoxide exposure—if detectors alarm, evacuate immediately.
Final Note: Implementing even two of these methods creates reliable heating without electricity. Start with sealing your primary living space and positioning thermal mass near windows—these require minimal investment but deliver immediate results during outages. As you build capabilities, add wood or solar systems tailored to your climate. Remember: the safest approach always combines multiple methods—passive solar design with emergency water heaters provides redundancy when storms hit. Begin preparations now; your future self will stay warm when the grid fails.