You’ve probably seen viral videos claiming you can build an oxygen generator in your garage using household items. When health concerns or emergency preparedness weigh on your mind, the idea of creating your own oxygen supply seems tempting. But here’s the urgent truth: attempting to generate oxygen at home for medical use is extremely dangerous and scientifically ineffective. The methods circulating online cannot produce the 90-95% purity required for breathing, often creating explosive mixtures or toxic contaminants instead.
This guide cuts through dangerous misinformation to reveal why DIY oxygen generation fails, what minimal educational demonstrations are actually safe, and—most importantly—how to access legitimate oxygen solutions when you truly need them. You’ll discover clear warning signs of hazardous tutorials, FDA-approved alternatives that actually work, and critical steps to protect yourself from viral DIY traps. If you’re researching how to generate oxygen at home due to health concerns, this information could prevent life-threatening consequences.
Why DIY Oxygen Generation Fails for Medical Use

Chemical Reactions Produce Contaminated, Low-Purity Oxygen
Combining hydrogen peroxide with yeast—a viral “hack”—creates oxygen mixed with water vapor, atmospheric nitrogen, and potential yeast byproducts. This mixture typically contains less than 50% oxygen, falling drastically short of the 90-95% purity required for medical therapy. The chemical reaction (2H₂O₂ → 2H₂O + O₂) also generates significant heat, causing dangerous pressure buildup in sealed containers that can rupture violently. Even laboratory-grade setups using potassium iodide catalysts cannot achieve medical purity due to unavoidable atmospheric contamination during gas collection.
Electrolysis Creates Explosive Gas Mixtures You Can’t Separate
Splitting water molecules (2H₂O → 2H₂ + O₂) requires high-voltage electricity and produces hydrogen and oxygen in a 2:1 ratio—a mixture so volatile it ignites from static electricity. Household setups lack the specialized platinum electrodes, explosion-proof enclosures, and gas separation membranes needed to isolate oxygen safely. Without professional-grade equipment, you’re essentially building a bomb: the hydrogen-oxygen combination has a detonation velocity of 2,700 m/s and can explode with just a spark from a light switch. Medical oxygen concentrators avoid this risk entirely by using pressure swing adsorption to extract oxygen from air—not water.
Plants Generate Negligible Oxygen for Human Needs
While photosynthesis (6CO₂ + 6H₂O + light → C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂) produces oxygen, a single mature houseplant creates only 5-10 mL of oxygen per hour—less than 0.1% of what an adult breathes. To match a standard 2 LPM medical concentrator’s output, you’d need over 20,000 actively photosynthesizing plants in perfect conditions. Plants also consume oxygen at night and cannot provide consistent, measurable flow rates. This method is biologically impossible for therapeutic use, yet it frequently appears in misleading “natural oxygen generator” videos.
Safe Educational Demonstrations Only
Hydrogen Peroxide Experiment: Strict Classroom Protocol
This demonstration proves oxygen exists in chemical reactions but cannot produce breathable gas. Use this exact procedure only under supervision:
Required Materials
– 100 mL of 3% pharmacy-grade hydrogen peroxide (never industrial strength)
– 1 teaspoon active dry yeast mixed with 2 tbsp warm water
– Heat-resistant glass container (no plastic)
– Glowing splint for testing
Critical Safety Execution
1. Place peroxide in container outdoors or under fume hood
2. Add yeast mixture and step back immediately—reaction starts in seconds
3. Hold glowing splint near (not in) gas stream to observe reignition
4. Discard mixture within 60 seconds—never attempt storage
Non-Negotiable Warnings
– NEVER use containers with narrow necks (pressure explosion risk)
– ALWAYS wear chemical splash goggles (peroxide causes corneal burns)
– ABORT if bubbling exceeds container height—indicates dangerous acceleration
Debunking Viral DIY Oxygen Generator Videos
Red Flags in Dangerous Online Tutorials
Watch for these critical warning signs that signal life-threatening advice:
– Claims of “95% pure oxygen” from vinegar/baking soda or saltwater electrolysis
– Instructions to pressurize gas into tanks (creates explosion hazards)
– Omission of hydrogen gas risks in water-splitting methods
– “Medical use” recommendations without prescription requirements
These videos often misuse terms like “oxygen generator” while showing setups that actually produce carbon monoxide or chlorine gas from impure chemicals. The glowing splint test confirms some oxygen presence but proves nothing about purity or safety for inhalation.
Real-World Consequences of DIY Attempts
Emergency rooms report injuries from:
– Chemical burns from concentrated peroxide (>12%) used in “stronger” hacks
– Flash fires when oxygen-enriched environments ignite from pilot lights
– Asphyxiation from nitrogen displacement during gas collection
– Electrocution from improvised high-voltage electrolysis rigs
One documented case involved a man who modified a water electrolyzer, causing a hydrogen explosion that shattered windows 30 feet away. Medical oxygen isn’t a chemistry project—it’s a regulated medical therapy.
Legitimate Medical Oxygen Solutions

FDA-Approved Oxygen Concentrators: How They Actually Work
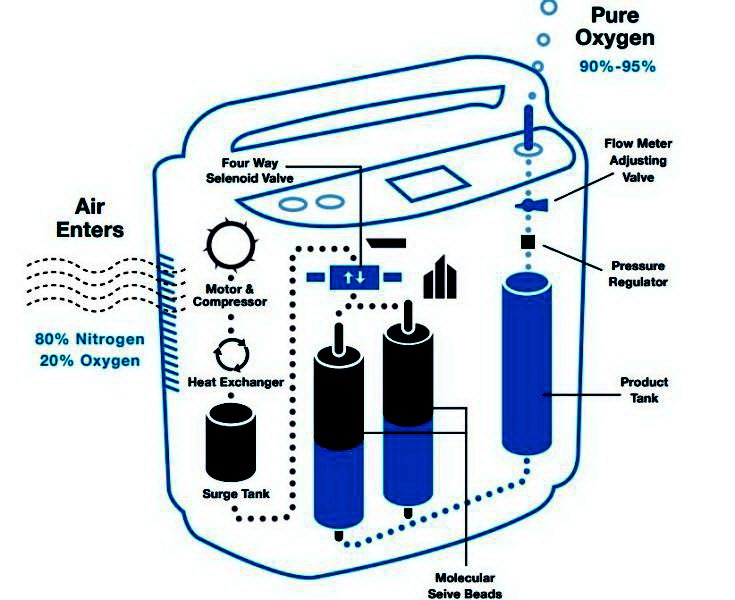
Unlike DIY methods, home concentrators use molecular sieve technology to extract oxygen from ambient air:
1. Compressors pull in room air (78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen)
2. Zeolite minerals adsorb nitrogen under pressure
3. Purified oxygen (90-95% concentration) flows to your cannula
4. Built-in sensors automatically shut down if purity drops below 85%
Why this beats DIY:
– Zero fire/explosion risks (no chemical reactions)
– Continuous 24/7 operation with standard wall power
– Prescription ensures correct flow rate (1-5 LPM) for your condition
– Medicare and most insurers cover 80%+ of costs for qualifying patients
Pre-Filled Oxygen Cylinders: Certified Safety
Medical suppliers deliver USP-grade oxygen in rigorously tested cylinders:
– Purity verification: Every tank batch undergoes gas chromatography
– Safety systems: Pressure relief valves and tamper-proof regulators
– Service protocol: Technicians inspect equipment during delivery
Unlike homemade gas, these cylinders come with emergency instructions, usage logs, and 24/7 clinical support. Never attempt to refill cylinders yourself—improper handling causes valve explosions.
Recognizing When You Need Professional Oxygen
Medical Warning Signs Requiring Immediate Evaluation
Contact your doctor if you experience:
– Shortness of breath walking 50 feet on level ground
– Oxygen saturation below 92% (confirmed by clinical pulse oximeter)
– Blue-tinged lips or fingernail beds (cyanosis)
– Morning headaches with daytime fatigue (sign of CO₂ retention)
Do not self-diagnose oxygen needs. Low blood oxygen can indicate heart failure, pulmonary embolism, or infections requiring different treatments. A single oxygen saturation reading isn’t diagnostic—your doctor will order arterial blood gas tests and pulmonary function studies.
Why Prescriptions Are Non-Negotiable
Oxygen therapy requires medical oversight because:
– Excess oxygen can suppress breathing in COPD patients
– Incorrect flow rates worsen sleep apnea complications
– Undiagnosed lung diseases may deteriorate with improper use
– Fire risks increase dramatically in oxygen-enriched environments
Your prescription specifies exact flow rates, usage duration, and safety protocols based on comprehensive testing—not internet guesses.
Emergency Preparedness for Oxygen Users
Power Outage Protection Strategies
If you rely on concentrators:
– Battery backups: Use medical-grade systems (e.g., Invacare 4-hour battery)
– Portable concentrators: Keep FAA-approved models (like Inogen One G5) charged
– Hospital backup plan: Register with local emergency management for priority power restoration
– Never use generators indoors—carbon monoxide kills faster than oxygen deprivation
Travel Oxygen Protocols
When leaving home:
– Book travel concentrators through your supplier 2+ weeks ahead
– Carry “oxygen in use” warning stickers for your vehicle
– Verify hotel electrical capacity (concentrators need dedicated 15A circuits)
– Always pack 24+ hours of backup cylinder supply
Cost Reality: DIY vs. Medical Solutions
Hidden Dangers in “Budget” DIY Approaches
While hydrogen peroxide seems cheap ($1/bottle), real costs include:
– $200+ for safety gear (explosion-proof container, oxygen sensors)
– $1,500+ ER visits for chemical burns or inhalation injuries
– Zero therapeutic value—all DIY methods fail purity standards
One ER study found 73% of DIY oxygen attempt injuries required hospitalization, costing $34,000+ on average.
Affordable Medical Oxygen Access
Most patients pay $0 out-of-pocket through:
– Medicare Part B coverage (80% after deductible)
– Medicaid programs in all 50 states
– Manufacturer assistance programs (e.g., Philips Respironics Patient Assistance)
– 36-month rental-to-ownership options under $100/month
Suppliers like Apria and Lincare provide free setup, maintenance, and emergency replacements—protections no DIY method can match.
Final Safety Imperatives
Generating oxygen at home for medical use is never safe or effective. The chemistry demonstrations that work in controlled labs cannot overcome atmospheric contamination, explosive byproducts, or purity limitations in home settings. Medical oxygen isn’t just “oxygen”—it’s a precisely calibrated therapy requiring professional oversight to prevent fire hazards, incorrect dosing, and delayed treatment of underlying conditions.
Reserve chemistry experiments strictly for educational purposes with proper supervision and disposal protocols. If you’re researching how to generate oxygen at home due to breathing difficulties, stop immediately and contact your healthcare provider. They’ll evaluate your needs through proper testing and prescribe solutions through certified medical suppliers—giving you the safe, reliable oxygen therapy you deserve without gambling with dangerous DIY methods.
Take action today: Call your doctor to discuss any breathing concerns, or contact the American Lung Association (1-800-LUNGUSA) for free oxygen therapy guidance. Your life depends on legitimate medical solutions—not viral videos.