Waking up gasping for air, struggling through foggy mornings, and battling relentless fatigue—these are the daily realities for millions with sleep apnea. If you’re searching for ways to stop sleep apnea naturally at home without CPAP, you’re not alone in seeking gentler solutions. While CPAP machines remain the gold standard treatment, evidence shows specific lifestyle modifications can significantly reduce symptoms for mild cases and complement treatment for more severe ones. This guide delivers actionable, research-backed strategies that target the root causes of your breathing interruptions, helping you reclaim peaceful sleep from the comfort of your bedroom tonight.
Pinpoint Your Sleep Apnea Type Before Starting Treatment
Before attempting any natural remedies, identifying your specific sleep apnea type determines which approaches will actually work for your situation. This isn’t just medical jargon—it directly impacts your treatment success rate and safety.
Obstructive vs Central Sleep Apnea: Know the Difference
Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA) occurs when throat muscles relax excessively during sleep, causing your airway to physically collapse. This type responds exceptionally well to positional therapy, lifestyle changes, and targeted exercises—making natural home remedies particularly effective.
Central Sleep Apnea (CSA) happens when your brain fails to send proper signals to breathing muscles. Natural approaches may offer some support, but this type typically requires medical supervision as lifestyle changes alone rarely provide complete relief.
Mixed Sleep Apnea combines both mechanisms, requiring a balanced strategy that addresses physical obstructions while supporting neurological breathing regulation. Attempting natural remedies without proper diagnosis could waste your time or worsen symptoms.
Match Remedies to Your Severity Level
Natural home treatments show remarkable effectiveness for mild sleep apnea (fewer than 15 breathing interruptions per hour), with many patients eliminating symptoms entirely through consistent lifestyle changes.
For moderate to severe cases (15+ interruptions hourly), natural methods serve as powerful complements to medical treatment—they enhance CPAP effectiveness, reduce required pressure settings, and improve overall sleep quality even when machines remain necessary.
Critical First Step: Never self-treat without a proper sleep study diagnosis. Attempting to cure sleep apnea naturally at home without CPAP for undiagnosed severe cases is dangerous and potentially life-threatening.
Stop Sleep Apnea Naturally Tonight With Position Fixes

Your sleeping position could be the hidden culprit worsening your breathing interruptions. Gravity becomes your enemy when you lie on your back, causing your tongue and soft tissues to collapse into your airway—triggering apnea events.
Transform Your Sleep Position in 24 Hours
Pillow Barrier Method: Arrange firm pillows in a U-shape around your body—place one behind your back, another supporting your front, and a third between your knees. This physical barrier prevents unconscious rolling onto your back during deep sleep. Most people notice reduced snoring within the first night.
Tennis Ball Technique: Sew a pocket onto the back of a tight-fitting shirt and insert a tennis ball. The discomfort when rolling onto your back trains your body within 2-3 weeks. Modern alternatives include wearable position trainers that vibrate gently when you roll onto your back.
Elevated Sleep Positioning: Stack pillows to achieve a 60-degree incline or invest in an adjustable bed base. This position uses gravity to keep tissues from collapsing backward into your airway. Test effectiveness by propping yourself with extra pillows for three nights—if snoring decreases and morning headaches improve, consider a permanent wedge pillow solution.
Eliminate Alcohol’s Sleep Apnea Trigger Immediately
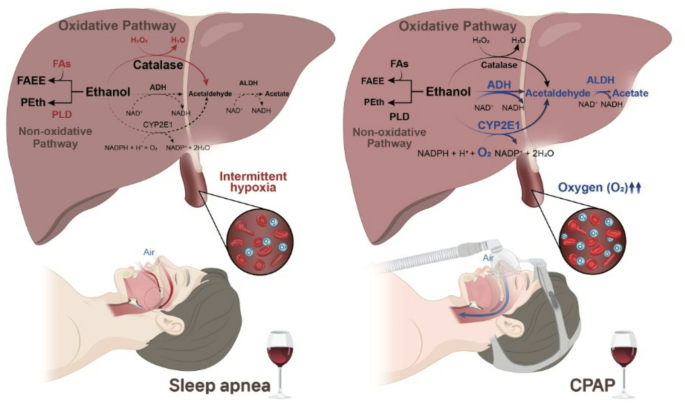
Alcohol’s relationship with sleep apnea goes far beyond causing snoring—it actually makes your airway collapse more frequently and severely, even with moderate consumption.
Alcohol’s Triple Threat to Your Nighttime Breathing
Muscle Relaxation: Alcohol acts as a powerful muscle relaxant, particularly affecting the muscles that keep your airway open. This relaxation persists for hours after your last drink.
Increased Collapsibility: Relaxed throat tissues become more prone to vibration (snoring) and complete obstruction (apnea episodes). One drink can double your apnea events for the entire night.
Enhanced Severity: Regular drinkers often develop more severe sleep apnea over time, as repeated airway trauma from alcohol-induced collapses causes permanent structural changes.
Practical Alcohol Protocol for Better Breathing
• Stop all alcohol consumption 4-6 hours before bedtime to allow your body to metabolize alcohol and restore normal muscle tone
• If you choose to drink socially, do so earlier in the evening with food, and never drink and sleep on your back
• Create alcohol-free bedtime rituals like herbal teas, gentle stretching, or reading to signal your body it’s time to wind down
Exercise Your Way to Fewer Apnea Events Tonight
Exercise offers benefits far beyond weight loss for sleep apnea sufferers. Even without shedding pounds, physical activity directly improves breathing patterns during sleep through multiple physiological mechanisms.
Targeted Exercise Strategies That Work
Walking Programs: Start with 30 minutes of brisk walking daily. This low-impact option suits most fitness levels and provides measurable symptom improvement within 4-6 weeks. Track your progress with a simple journal noting snoring intensity and morning energy levels.
Strength Training: Focus on upper body and core exercises. Stronger respiratory muscles support better breathing mechanics during sleep. Start with simple bodyweight exercises like push-ups and planks, gradually increasing to 3 sets of 10-15 repetitions.
Yoga and Breathing Exercises: Specific yoga poses strengthen throat muscles while breathing techniques improve overall respiratory function. Practice “ujjayi breathing” for 5 minutes twice daily—this technique tones the soft palate and throat muscles critical for maintaining open airways.
Implementation Schedule: Begin with 15-minute sessions, gradually increasing to 45-60 minutes daily. Consistency matters more than intensity—daily moderate exercise outperforms sporadic intense workouts for reducing apnea events.
Review Medications That Worsen Sleep Apnea
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/how-medications-may-affect-sleep-apnea-3014683-final-75e32aaeff0a404da928ec4b51c80e5b.png)
Many common medications can trigger or worsen sleep apnea symptoms. A thorough medication review with your doctor often reveals surprising culprits that might be sabotaging your breathing.
Sleep Apnea-Exacerbating Medications to Flag
Benzodiazepines (Xanax, Valium): Prescribed for anxiety or insomnia, these drugs relax airway muscles and depress breathing centers in the brain.
Sleeping Pills (Ambien, Lunesta): While intended to improve sleep, they can increase apnea events by suppressing the natural arousal response that triggers breathing.
Opioid Pain Medications: These powerful pain relievers significantly depress respiratory drive and can cause central sleep apnea even in previously unaffected individuals.
Antihistamines: Over-the-counter allergy medications like Benadryl contain sedating properties that worsen airway obstruction.
Medication Optimization Strategy
Schedule a dedicated appointment with your prescribing physician specifically to discuss sleep apnea. Bring a complete list of all medications, including supplements and over-the-counter drugs. Ask about non-sedating alternatives for your conditions—melatonin supplements might replace prescription sleep aids, or non-drowsy antihistamines could substitute for sedating allergy medications.
Strengthen Airway Muscles With Daily Exercises
Myofunctional therapy—targeted exercises for throat and mouth muscles—offers a drug-free way to reduce apnea events by building stronger, more resilient airway tissue that resists collapse during sleep.
3-Minute Daily Exercise Routine
Tongue Strengthening: Push your tongue firmly against the roof of your mouth and hold for 10 seconds. Repeat 5 times. Then slide your tongue along your upper palate from front to back 10 times.
Throat Toning: Say “ah” for 20 seconds while keeping your throat open wide. Perform exaggerated chewing motions for 1 minute. These simple exercises can be done while brushing your teeth.
Lip Seal Practice: Hold a spoon handle between your lips for 30 seconds, gradually increasing duration. This strengthens facial muscles that support proper airway positioning during sleep.
Perform these exercises for 10 minutes twice daily—once in the morning and once before bed. Most people notice measurable improvements in snoring and breathing within 8-12 weeks of consistent practice.
Create a Sleep Environment That Supports Natural Breathing
While environmental changes won’t cure sleep apnea alone, they create optimal conditions for your other interventions to work effectively and comfortably throughout the night.
Humidifier Setup: Maintain bedroom humidity between 40-50% to reduce morning throat dryness and irritation. Clean humidifiers weekly to prevent mold growth that could worsen breathing issues. Place the unit at least 3 feet from your bed for optimal air distribution.
Temperature Control: Set your bedroom to 65-68°F (18-20°C) to promote deeper sleep and reduce position changes that might trigger apnea events. Cooler temperatures help regulate your body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
Complete Darkness: Use blackout curtains and cover electronic lights to support natural melatonin production. Even small amounts of light can fragment sleep and potentially increase apnea frequency.
Track Your Progress and Know When to Seek Help
Natural sleep apnea remedies require careful monitoring to ensure safety and effectiveness. Establish clear protocols before beginning any home treatment to measure what’s working and when to consult a professional.
Essential Tracking Methods
• Record snoring intensity nightly (ask your partner for observations)
• Track daytime sleepiness using the Epworth Sleepiness Scale
• Note morning headache frequency and cognitive clarity
• Monitor sleep quality on a 1-10 scale each morning
Warning Signs Requiring Medical Attention:
– Worsening daytime sleepiness despite treatment
– New cardiovascular symptoms (chest pain, irregular heartbeat)
– Severe morning headaches or confusion
– Breathing difficulties during wakefulness
Most people see improvements within 4-6 weeks of consistent effort. If you notice no changes by then, schedule a follow-up with your sleep specialist to discuss additional treatment options.
Natural sleep apnea remedies offer genuine hope for mild cases and powerful support for more severe ones. While these strategies require dedication, the payoff—peaceful, restorative sleep—justifies every effort. Remember: your journey to better breathing starts with a single step, whether that’s sleeping on your side tonight or scheduling that crucial sleep study tomorrow.