Power outages strike without warning, leaving homes dark and families vulnerable. Whether you’re facing hurricane season, winter storms, or aging electrical grids, the right generator transforms chaos into comfort. But with countless options flooding the market, selecting the perfect backup power source feels overwhelming.
This guide cuts through the confusion, delivering practical steps to match your specific needs with the ideal generator. You’ll learn to calculate exact power requirements, navigate fuel choices, and avoid costly sizing mistakes. By the end, you’ll confidently select a generator that keeps your family safe and comfortable during any outage.
Match Your Generator Type to Outage Patterns
Portable Generators for Occasional Power Loss
When outages happen just a few times yearly, portable generators deliver the most practical solution. These gasoline-powered units require manual setup during emergencies but cost significantly less than permanent systems. Expect to pay $500-$4,000 for 3,000-12,000 watts of power—enough to run 3-8 essential circuits like refrigeration, lighting, and well pumps.
Critical limitation: You must operate portable generators outdoors, 20+ feet from windows and doors to prevent deadly carbon monoxide poisoning. Never run them in garages, basements, or enclosed spaces. If you experience frequent outages requiring regular generator use, you’ll quickly appreciate the convenience of automatic systems.
Standby Generators for Frequent or Extended Outages
When the power goes out more than four times annually, standby generators become the smarter investment. These permanently installed systems activate automatically within 10-30 seconds of detecting an outage, connecting directly to your home’s electrical panel and natural gas or propane supply.
Key differentiator: Standby units range from 7,000-48,000 watts, with most homes requiring 12,000-22,000 watts for whole-house coverage including central air conditioning. While the $5,000-$23,000 installed price tag seems steep initially, the peace of mind during extended outages proves invaluable. Insurance companies often offer 5-10% premium discounts for professionally installed systems.
Inverter Generators for Sensitive Electronics
If you need to power computers, medical equipment, or entertainment systems during outages, inverter generators solve the “dirty power” problem of conventional units. These advanced models produce clean, stable electricity by converting DC to AC power through sophisticated electronics.
Pro tip: Inverter generators adjust engine speed based on demand, running quieter (55-75 decibels) and consuming 20-30% less fuel than conventional models. While portable inverters cost $800-$4,000 for 2,000-7,000 watts, standby inverter systems command premium pricing 20-30% higher than standard alternatives.
Calculate Your Exact Power Requirements

Identify Essential Circuits Before Shopping
Start by listing appliances critical for safety and comfort during outages. Remember the crucial distinction between starting watts (needed briefly when motors engage) and running watts (continuous operation):
- Refrigerator/freezer: 1,200 starting watts / 800 running watts
- Sump pump: 2,150 starting watts / 1,050 running watts
- Central AC (3-ton): 3,800 starting watts / 2,500 running watts
- Well pump (1HP): 2,000 starting watts / 1,000 running watts
Common mistake: Homeowners often overlook heating systems requiring 500-5,000 watts depending on type. During winter outages, this becomes your highest priority after refrigeration. Skip power-hungry items like electric water heaters (4,500 watts) and clothes dryers (5,000 watts) unless you’ve budgeted for a large standby system.
Apply the 25% Buffer Rule
After totaling your essential circuit requirements, add 25% extra capacity. This buffer accommodates simultaneous startup surges when multiple appliances engage at once—a scenario that trips undersized generators.
Smart sizing shortcut: For homes under 2,500 square feet needing partial backup, 7,000-12,000 watts typically suffices. Whole-house coverage requires 3-5 watts per square foot—meaning a 2,500 sq ft home needs minimum 12,500 watts. Skip online calculators that overestimate by 20-30%; instead, create your own appliance inventory with both running and starting wattage.
Select the Right Fuel Type for Your Location
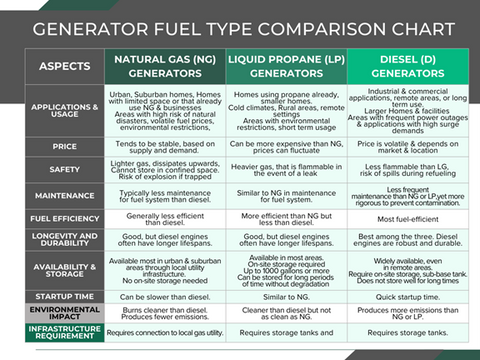
Natural Gas for Urban/Suburban Reliability
If your home connects to municipal gas service, natural gas generators offer unlimited runtime without refueling concerns. These systems consume 100-250 cubic feet per hour at half load and activate automatically during outages.
Critical consideration: Natural gas availability remains generally reliable during widespread disasters due to underground infrastructure, but professional gas line installation adds $1,000-$3,000 to your project. Verify with your utility company whether gas service continues during electrical grid failures in your area.
Propane for Rural Independence
Rural homeowners without natural gas service should consider propane systems using 250-1,000 gallon tanks providing 48-200 hours of continuous operation. Propane’s indefinite storage life makes it ideal for infrequent outages.
Pro tip: Install an automatic tank gauge that alerts you when levels drop below 20%. During extended outages, schedule refills before your tank runs dry—propane suppliers often face shortages when demand spikes after major storms.
Diesel for Extreme Conditions
In regions with harsh winters or frequent, prolonged outages, diesel generators provide superior reliability. These commercial-grade units offer excellent cold-weather performance and 18-24 month fuel shelf life with proper stabilizers.
Warning: Diesel requires specialized storage solutions and regular fuel testing. Only consider this option if you experience outages exceeding 72 hours regularly or need maximum reliability for medical equipment.
Plan Your Installation for Safety and Compliance
Transfer Switch Selection Made Simple
Your transfer switch determines how safely and conveniently your generator connects to home circuits. Manual transfer switches ($200-$800) require you to flip switches during outages, while automatic models ($400-$2,000) provide seamless transitions.
Critical safety note: Never connect generators directly to household outlets—this creates deadly “backfeed” conditions that can electrocute utility workers. Whole-house transfer switches connect to your main electrical panel, while essential-circuit models protect 6-16 critical circuits. Most homeowners benefit from 200-amp automatic switches.
Location Requirements You Can’t Ignore
Standby generators require specific placement to ensure safety and code compliance. Install units on concrete pads 3-6 inches thick extending 6 inches beyond the generator footprint. Maintain minimum clearances of 5 feet from house openings, 3 feet from combustibles, and 18 inches from walls.
Neighbor-friendly tip: Position generators away from bedrooms and property lines. Sound-attenuated enclosures reduce noise to 55-75 decibels—comparable to normal conversation—but proper placement prevents complaints during extended outages.
Budget for Total Ownership Costs

Realistic Cost Breakdowns
Portable generator systems cost $1,000-$5,800 total, including:
– Generator: $500-$4,000
– Transfer switch: $200-$800
– Installation: $300-$1,000
Standby generator systems require $5,000-$23,000 for:
– Generator: $3,000-$15,000
– Installation: $2,000-$8,000
Hidden costs: Budget $500-$1,500 for concrete pads, $1,000-$4,000 for propane tanks, and $200-$800 for permits. Annual maintenance costs $200-$400 for standby units and $50-$100 for portables.
Smart Timing for Purchase
Buy generators during off-peak seasons (spring or fall) when dealers offer better pricing and faster installation scheduling. Avoid hurricane season and winter storm periods when demand spikes create shortages and delays.
Planning tip: Allow 4-12 weeks for standby generator installation including permits, scheduling, and utility coordination. If severe weather threatens, portable generators provide immediate availability but require manual operation.
Final Recommendation: Your perfect generator balances outage frequency, essential power needs, and budget constraints. Start by calculating exact wattage requirements with a 25% buffer, then select fuel based on local availability. Prioritize professional installation for safety and warranty compliance—this isn’t a DIY project. Schedule annual maintenance to ensure decades of reliable service when you need it most.
Don’t wait for the next storm warning to begin your generator selection process. The right backup power system transforms disruptive outages into minor inconveniences, keeping your family safe and comfortable no matter what the weather brings.