Waking up gasping for air or struggling through a workout due to wheezing shouldn’t be your normal. If you’re searching for how to treat asthma at home, you’re not alone—over 25 million Americans manage this condition daily. The good news? With the right home strategies, you can reduce reliance on emergency inhalers by up to 50% and transform your living space into an asthma-friendly sanctuary. This guide delivers evidence-based, actionable steps you can implement today to breathe easier without constant medical intervention.
Master Your Emergency Asthma Attack Response

Execute the 10-Second Rescue Inhaler Protocol
When symptoms strike, proper inhaler technique makes the difference between rapid relief and prolonged suffering. Shake your albuterol inhaler vigorously for 5-10 seconds, then completely exhale before placing your lips around the mouthpiece. Press down while inhaling deeply for 3-5 seconds, hold your breath for 10 seconds, then slowly exhale. This precise method delivers 30% more medication to constricted airways than improper use.
If symptoms persist after 2-4 puffs, repeat every 20 minutes for one hour—but never exceed your prescribed maximum. Keep your rescue inhaler visible on your nightstand, kitchen counter, and living room table so it’s never more than 3 feet away when you need it most.
Recognize When to Call 911 Immediately
Don’t wait when you notice blue-tinged lips or fingernails, inability to speak complete sentences, or no improvement after maximum rescue inhaler use. While waiting for emergency help, sit upright with shoulders relaxed and loosen tight clothing—lying flat restricts your diaphragm and worsens breathing difficulties. Have someone time your breaths; fewer than 10 breaths per minute or more than 30 indicates critical severity requiring immediate intervention.
Optimize Your Daily Medication Routine
Perfect Your Spacer Device Technique
Using a spacer with your inhaler boosts medication delivery by 50-70%, yet most people skip this crucial step. Attach your inhaler to the spacer, exhale fully away from the device, then place your lips tightly around the mouthpiece. Press the inhaler once and breathe in slowly for 5-6 seconds—counting “one-Mississippi, two-Mississippi” helps maintain proper pace. Hold for 10 seconds before exhaling.
Clean your spacer weekly with warm, soapy water and air-dry completely. Replace every 6-12 months or immediately if cracked. Many insurance plans cover spacers at little or no cost—ask your provider to avoid this common oversight.
Track Controller Medication Effectiveness
Mark your controller inhaler with the fill date and replace when the counter shows 20 doses remaining—never wait until it’s empty. Take inhaled corticosteroids like fluticasone at the same time daily, preferably with breakfast, and always rinse your mouth thoroughly afterward to prevent oral thrush. Store all inhalers at room temperature away from bathroom humidity and direct sunlight, which degrades medication potency.
Transform Your Home Into an Asthma Sanctuary
Eliminate Bedroom Allergen Hotspots

Your mattress likely harbors 1-10 million dust mites—major asthma triggers. Encase your mattress, box spring, and pillows in zippered allergen-proof covers immediately. Wash all bedding weekly in water heated to at least 130°F, followed by high-heat drying. Replace bedroom carpeting with hard flooring or vacuum twice weekly using a HEPA-filtered machine.
Install a HEPA air purifier in your bedroom with a Clean Air Delivery Rate (CADR) equal to at least two-thirds of your room’s square footage. Keep windows closed during high pollen seasons and monitor indoor humidity with a digital hygrometer, maintaining levels between 30-50% to prevent mold and dust mite growth.
Neutralize Cooking and Cleaning Triggers
Avoid aerosol sprays and strong chemical cleaners that irritate sensitive airways. When cooking, always turn on exhaust fans before starting and keep them running for 30 minutes after finishing. Choose fragrance-free detergents and avoid scented candles or air fresheners that release volatile organic compounds.
Implement Breathing Techniques for Instant Relief
Apply Pursed Lip Breathing During Activity
Struggling during exercise? Inhale through your nose for 2 counts, then exhale through pursed lips (as if blowing out a candle) for 4 counts. This simple technique keeps airways open longer, reduces breathlessness by 40%, and prevents hyperventilation. Practice during daily activities like climbing stairs until it becomes automatic during symptom flare-ups.
Practice Diaphragmatic Breathing Daily
Lie on your back with knees bent, placing one hand on your chest and another below your ribcage. Inhale slowly through your nose, focusing on expanding your belly rather than your chest. Hold for 2-3 seconds, then exhale slowly through pursed lips. Start with 5-minute sessions twice daily—this strengthens respiratory muscles and improves oxygen exchange by 20%.
Manage Triggers Through Diet and Monitoring
Track Food and Symptom Connections
Maintain a detailed food diary noting meals alongside symptoms and peak flow readings. Common trigger foods include sulfites in wine and dried fruits, MSG in processed foods, and histamine-rich items like aged cheeses. Never attempt elimination diets without medical supervision—nutritional deficiencies can worsen asthma control.
Focus on anti-inflammatory foods: salmon (2-3 grams of omega-3s per 3.5-ounce serving), walnuts (2.5 grams per 1/4 cup), and vitamin C-rich red bell peppers (95mg per 1/2 cup). Stay hydrated with 8-10 glasses of water daily to thin mucus secretions.
Establish Your Personal Peak Flow Baseline
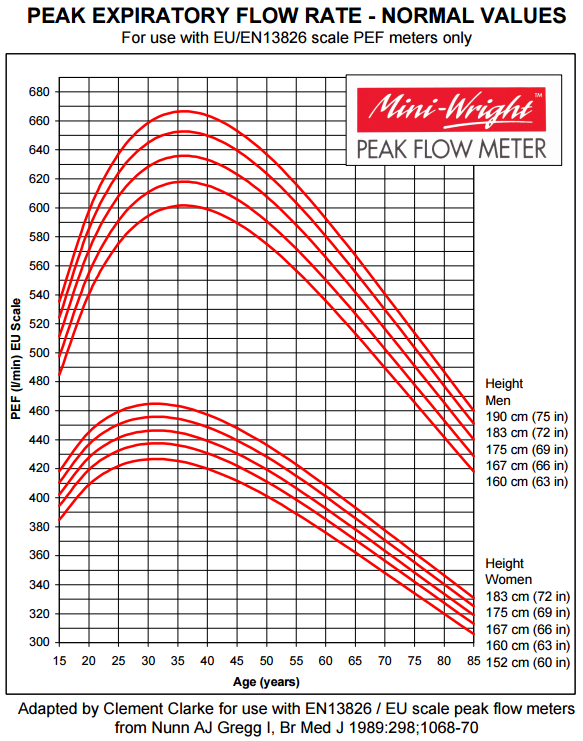
Take morning and evening peak flow readings for 2-3 weeks during good control to establish your personal best. Your green zone (80-100% of personal best) indicates good control. Yellow zone (50-79%) means adjust medications per your action plan. Red zone (below 50%) requires immediate medical attention. Share this data with your doctor to refine your treatment strategy.
Optimize Exercise and Sleep for Better Control
Prevent Exercise-Induced Symptoms
Use your rescue inhaler 15 minutes before physical activity to prevent bronchospasm. Begin with 10-15 minutes of gradual warm-up before intense activity. Choose indoor swimming pools when possible—the humidified air is less irritating to sensitive airways. During cold weather, wear a scarf over your mouth to warm incoming air.
Create an Asthma-Friendly Sleep Environment
Maintain bedroom temperatures between 68-72°F year-round. Elevate the head of your bed 6-8 inches using bed risers to reduce nighttime reflux that triggers symptoms. Take evening controller medications 1-2 hours before bedtime for optimal overnight effectiveness and avoid eating within 3 hours of sleep.
Reduce Treatment Costs Without Sacrificing Quality
Maximize Medication Savings
Utilize manufacturer discount programs for brand-name medications—they often reduce costs by 50-75%. Compare pharmacy prices using apps like GoodRx, which frequently beat insurance copays. Consider 90-day supplies for maintenance medications to significantly reduce per-dose costs. Ask your doctor about generic alternatives for controller medications.
Review your insurance formulary annually during open enrollment to ensure your medications remain covered. Document medical necessity when appealing denied claims—your healthcare provider can support requests for essential medications.
While these home strategies significantly improve asthma control, they’re designed to complement—not replace—professional medical care. Schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider and update your action plan as needed. The goal isn’t perfect control, but consistent, manageable symptoms that allow you to live fully and breathe freely. By implementing these evidence-based home treatments, you’ll reduce emergency inhaler use, minimize nighttime symptoms, and gain confidence in managing your asthma independently.