Mice can infiltrate your home through openings as small as a pencil’s width—just 1/4 inch—making even the tiniest gaps potential invasion routes. If you’ve discovered droppings in your pantry, heard scratching in walls after dark, or spotted greasy rub marks along baseboards, your home is already vulnerable. This comprehensive guide provides the exact steps to seal your home from mice permanently, using professional inspection techniques and proven sealing methods that address both current vulnerabilities and future prevention.
You’ll learn how to identify hidden entry points most homeowners miss, select the right materials for each gap type, and implement a strategic sealing order that maximizes effectiveness. By the end of this guide, you’ll have transformed your home into an impenetrable fortress against rodents, eliminating the conditions that attract mice while creating physical barriers they cannot breach.
Why Standard Pest Control Fails Against Mouse Entry
The 1/4-Inch Rule Every Homeowner Must Know
Mice possess extraordinary physical capabilities that make them formidable invaders. Their flexible ribcages allow them to compress their bodies through openings measuring just 1/4 inch wide—the diameter of a standard pencil. This minimal clearance requirement means seemingly insignificant gaps around pipes, wiring, and construction joints become convenient entry points for these persistent rodents.
When inspecting your home, focus on areas where different building materials meet, such as where siding connects to foundation walls or where pipes penetrate through floors. These transition points often develop microscopic gaps over time that mice exploit. Remember: if you can fit a pencil through it, mice can too.
Common Misconceptions About Mouse Prevention
Many homeowners make critical mistakes when attempting to seal their homes from mice. Spraying pesticides or setting traps addresses symptoms but ignores the root cause—entry points. Others mistakenly believe that sealing only the largest gaps is sufficient, not realizing mice can navigate through multiple small openings to reach food sources.
The most effective approach combines thorough inspection with strategic sealing of every potential entry point, regardless of size. This exclusion method creates permanent barriers that prevent future infestations rather than merely reacting to current problems.
Targeted Interior Inspection Techniques
Kitchen Cabinet Vulnerability Hotspots
Begin your inspection in the kitchen where food attracts mice most. Remove all items from lower cabinets and use a flashlight to examine:
- Back walls where plumbing pipes enter through cabinet holes
- Floor junctions where cabinets meet flooring materials
- Corner gaps where cabinet sides meet walls
- Under-sink areas around drain and supply line penetrations
Check for dark rub marks indicating regular mouse traffic—these greasy streaks appear where mice repeatedly squeeze through openings. Pay special attention to areas behind appliances like refrigerators and dishwashers where gaps often develop.
Closet and Storage Area Entry Points
Closets on exterior walls often harbor overlooked vulnerabilities. Focus your inspection on:
- Baseboard gaps where trim meets flooring
- Carpet edges along walls where gaps may exist beneath
- Built-in shelving connection points to walls
- Floor corners where settling creates separations
Use your fingers to feel for drafts along baseboards—any noticeable airflow indicates a potential entry point. Mice prefer quiet, undisturbed areas like rarely used closets for their access routes.
Exterior Vulnerability Hotspots
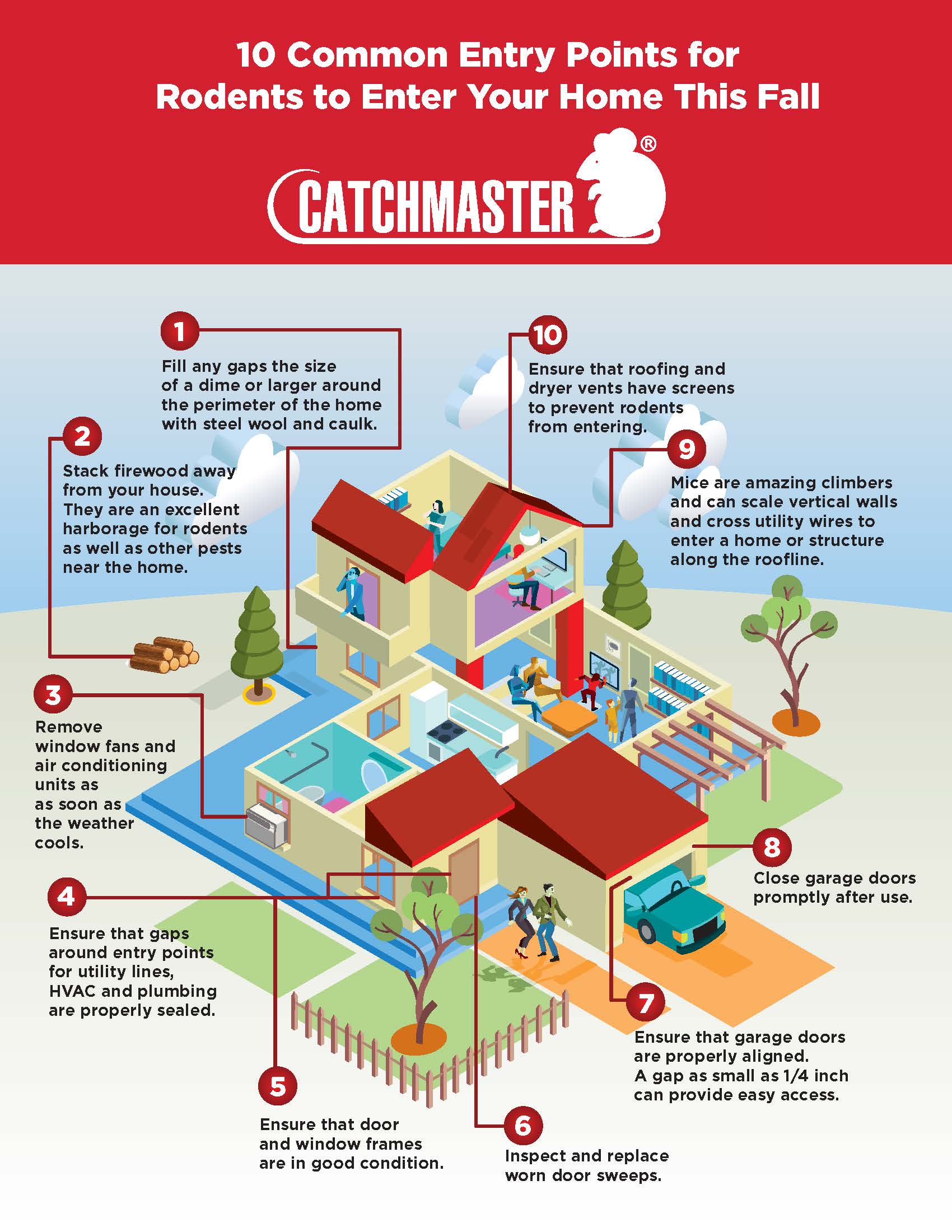
Foundation-to-Ground Interface Gaps
Walk your home’s entire foundation perimeter with a flashlight, examining:
- Material junctions where siding meets foundation
- Expansion joint gaps in concrete foundations
- Crack formations from settling or structural movement
- Grade separations where ground meets foundation walls
Pay special attention to areas where pipes or wires enter the home—these utility penetrations often develop gaps over time. Feel for drafts around foundation vents and check that all screening remains intact without tears.
Window and Door Weak Points
Examine every window and door on your home’s exterior:
- Weather stripping gaps along door frames
- Window casing separations where trim meets siding
- Sill plate cracks beneath door thresholds
- Frame-to-wall gaps around the entire perimeter
Test weather stripping effectiveness by closing doors on dollar bills—if bills slide out easily, mice can squeeze through. Focus on older windows and doors where materials have deteriorated over time.
Professional-Grade Sealing Materials

Caulk Selection by Location and Gap Size
Choose appropriate caulk types based on specific needs:
- Silicone caulk for exterior gaps exposed to weather
- Polyurethane sealant for larger foundation gaps
- Acrylic latex for interior paintable applications
- Expanding foam for irregular gaps and voids
Apply caulk in continuous beads without breaks, ensuring complete gap coverage. Tool the caulk smooth for maximum adhesion and appearance. For gaps wider than 1/4 inch, install backer rod before applying caulk to create a proper foundation for the sealant.
Steel Wool and Hardware Cloth Solutions
Combine materials for maximum effectiveness:
- Grade 0000 steel wool (fine) for small cracks and gaps
- 1/4-inch mesh hardware cloth for vents and larger openings
- Galvanized steel for areas requiring rodent resistance
- Seal over packed steel wool with caulk or foam for permanent installation
Mice cannot chew through properly installed steel wool, making it an effective deterrent when combined with other sealing materials. Cut hardware cloth slightly larger than openings and secure with appropriate fasteners for each surface type.
Step-by-Step Sealing Protocol
Priority Sealing Order for Maximum Effectiveness
Follow this sequence for optimal results:
- Address largest gaps first—anything larger than 1/2 inch
- Seal obvious entry points around utilities and pipes
- Tackle weather stripping on doors and windows
- Finish with smaller cracks and cosmetic gaps
Begin with exterior vulnerabilities before moving indoors. This outside-in approach prevents creating pressure that might force mice deeper into your home during the sealing process.
Foundation Gap Treatment Process
For gaps between foundation and ground:
- Clean the area thoroughly, removing debris and old caulk
- Apply backer rod for gaps wider than 1/4 inch
- Install caulk in continuous beads without breaks
- Tool smooth for professional appearance and maximum seal
Check foundation vents to ensure all screening remains intact and properly secured. Replace torn or damaged screens with 1/4-inch mesh hardware cloth.
Food Source Elimination Tactics

Kitchen Food Security Upgrades
Transform your kitchen into a mouse-resistant zone:
- Transfer all dry goods to airtight containers within 48 hours
- Store pet food in sealed bins, never leaving bowls out overnight
- Empty garbage daily, using cans with tight-fitting lids
- Clean crumbs from counters, floors, and appliance areas daily
Focus on areas where crumbs accumulate—behind appliances, under cabinets, and along baseboards. Install under-sink cabinet doors if missing to prevent easy access to plumbing areas.
Exterior Attractant Removal
Modify your property’s exterior to discourage mouse habitation:
- Store garbage in sealed containers at least 10 feet from the house
- Remove fallen fruit from trees and garden areas promptly
- Stack firewood at least 20 feet from the home’s foundation
- Eliminate debris piles that provide nesting materials
Maintain a 2-foot vegetation-free zone around your home’s perimeter for enhanced protection. Trim tree branches at least 6 feet away from the roofline to prevent aerial access.
Post-Sealing Verification System
Monitoring for Success Indicators
Install these detection methods after sealing:
- Snap traps in attic and basement areas to verify exclusion success
- Glue boards along walls in suspect areas
- Regular inspections every 2 weeks for the first 3 months
- Droppings check in previously active areas
Continue monitoring until 60 days pass without signs of mouse activity. Place indicators in strategic locations where mice would travel if attempting re-entry.
Maintenance Schedule for Long-Term Protection
Prevent future infestations through ongoing maintenance:
- Quarterly inspections of all sealed areas, especially after seasonal changes
- Annual weather stripping replacement on frequently used doors
- Seasonal caulk touch-ups in high-movement areas
- Immediate sealing of any new gaps discovered during routine checks
Create a visual log of all sealed areas with photos and notes to track effectiveness over time. Schedule seasonal inspections in spring (after winter damage assessment) and fall (before rodent season begins).
When to Call Professional Help
Safety-Critical Situations Requiring Experts
Contact pest control professionals immediately when:
- Access is unsafe—such as steep roofs or confined crawl spaces
- Infestation is confirmed with multiple active areas or nesting sites
- Health concerns exist from accumulated droppings in hard-to-reach areas
- Structural damage has occurred requiring specialized repair
Professionals possess the equipment and expertise to safely address these challenging scenarios while ensuring complete exclusion.
Successfully sealing your home from mice requires methodical inspection, appropriate materials, and consistent maintenance. By following this systematic approach, you’ve created multiple barriers that mice cannot penetrate while eliminating the attractants that draw them near. Remember that mouse exclusion is an ongoing process—regular inspections and prompt sealing of new gaps ensure your home remains rodent-free for years to come. The initial investment of time and materials pays dividends through improved home hygiene, protection of food supplies, and peace of mind that your living environment remains secure against these persistent invaders.